The steel structures are constructed by properly connecting the available standard sections. The connections are an important part of steel structure and are designed more conventionally than any individual members. There is a discrepancy between the actual behavior and the analysis of steel structure is large, therefore the connections are complex to analyze and design. When the structural member fails in case of overloading then there is a general practice to prefer the individual member rather than the connections, therefore this kind of practice affects many structural members. The cost of structural steel consists of major portion of connections and that is the reason primary importance should be given to the design of connections for safety and economy of structure.
The connections are generally provided in the following cases:
- When there is the requirement to cater the heavy load and long span then the built-up sections are to be provided. In this case, this section should be connected together to get a good section.
- In case of longer span, the length of standard section needs to be connected with other section. In this case to connect the multiple sections proper design of connections are important.
- The different members need to be connected at the end (for example secondary beams to be connected to primary beam, column, footings, etc).
The classification in the connections provided in the steel structure is as follows:
- Riveted connections
- Bolted connections
- Welded connections
- Pinned connections
Riveted connections:
The riveted connections are nowadays obsolete. The understanding of this type of connections for the strength evaluation and rehabilitation for an older structure is essential. While the connection procedure for riveted connections is same as that of the bolted connections.
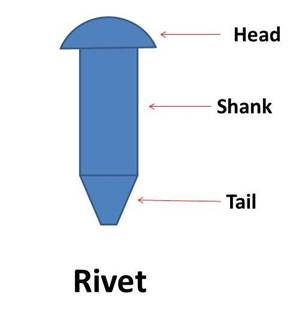
Rivet:
A rivet is made up of round ductile steel bar which is called as ‘shank’ and with a head at the one end. It is made up of mild steel or high tensile steel.
Riveting:
Riveting is the particular method of connecting together pieces of metal. This process is conducted by inserting the ductile metal pins called as rivet into the holes of pieces to be joined and formed a head at the end of the rivet to prevent each metal piece from coming out.
The shank of the rivet is made up of the length to the extent through the different parts which is to be connected and with sufficient extra length for a second head to be made at the other end.
The rivets are generally classified as follows:
- Hot driven rivets: The rivets which are driven in the hot conditions
- Shop rivets: The rivets which are placed in workshop
- Field rivets: The rivets which are placed in the site/field.
- Cold driven rivets: Since high pressure is required to form the head at room temperature this type of rivet is limited.
Clamp action:
When hot driven rivets are properly cooled down then the diameter and shank length get reduced. Because of this, the compression of the plates occurs and that results in friction between the plates, this process is called as clamp action.
Disadvantages of riveted connections are as follows:
- It is associated with very high level of noise pollution
- There is a need to heat the rivet till red hot color.
- Skilled labors are necessary to inspect the connection.
- The cost to remove the poorly installed rivet is very high.
- The high-cost installation in the connection.
Bolted Connection:
Most commonly used connections include the bolted connections. This connection has the advantage of flexibility in assembling parts of the structure as well as dissembling it and which is necessary if there is inspection or some routine maintenance. This type of connections is applicable for members subjected to tension or shear or both tension and shear.
A bolt is a metal pin with a head formed at one end and the shank threaded at the other end so that nut can be received. Generally, the bolts are used to connect the pieces of metals by inserting them through the holes in the metals; at the threaded end, nuts should be tightened.

The advantages of bolted connections are as follows:
- The process of erection of structure can be made faster.
- Skilled labors are not necessary.
- Connections do not involve the noise.
- Requirement of labors is less.
- Immediate use of structure is possible in case of bolted connection.
- The alternative arrangement of structural members is possible if required.
- Lesser working area is required.
The disadvantages of bolted connections are as follows:
- The material cost is very high.
- Due to the area reduction at the root of the thread and due to concentration of stress, the tensile strength of this type of connection is reduced.
- Bolts get loose if it is subjected to vibrations or shocks.

Classification of bolted connections:
The classifications of bolted connections are made on the basis of resultant force transferred, type of force and force mechanism.
On the basis of resultant force transferred:
- Concentric connections: When the load of structural member passes through the CG of the section then this type of connections are made.
- Eccentric connections: Whenever the resultant force is acting away from the CG of the connections.
- Moment resisting connections: Whenever the connections are subjected to moments.
On the basis of type of force:
- The connections are classified as shear connections when the transfer of load occurred through shear. Example: lap joint, butt joint
- Tension connection: Whenever the transfer of load occurred through tension on the bolts.
- Combined tension shear connections: whenever the bracket connection is used to connect the inclined member to the column of the structure.
On the basis of force mechanism:
- Bearing type connections: To transfer the force bolts bear against the hole
- Friction type connections: Due to tensioning of the bolts the force is transferred through friction between the plates.
The design philosophy:
The conventional method to analyze the connection is based on the following conditions:
- The deformation of the connection is ignored as the connected elements of the structures is considered as rigid connections
- The connectors used to connect different elements of the section behave like linear – elastic way until it fails.
- The ductility property of connectors of the structures is unlimited.




Comments are closed.